SpeakHDL is an FPGA Design Entry Tool
SpeakHDL is an FPGA Design Entry Tool:
SpeakHDL is a command based FPGA design entry tool focused on ease of use and FPGA rapid prototyping. The novel approach of SpeakHDL is that it utilizes both procedural programming techniques and user voice or hotkey commands to increase FPGA design productivity. SpeakHDL utilizes an API library of procedure calls implemented in native VHDL that generalize a state machine interface as a hardware abstraction layer. It then uses this hardware abstraction layer to interconnect components and implement sequential logic circuits such as state machines, fifos, counters, ect.
Under the hood, SpeakHDL utilizes a
patented design strategy
with a
flat design architecture
which makes procedural programming useful for synthesizable FPGA design. The design pattern, which is essentially a hybrid between a
facade design pattern
and a
state design pattern
, masks much of the FPGA design complexity. However, the design pattern can be somewhat tedious to implement using traditional
RTL
coding techniques. SpeakHDL adds many usability features to the design pattern. It provides a way to map voice commands and hotkey sequences to VHDL procedure calls without imposing a steep learning curve on the user.
Using a State Machine as a Facade Object
Using a State Machine as a Facade Object
A meaningful FPGA design pattern must perform a variety of tasks. The design pattern should:
- lower the complexity of the FPGA design for the developer
- provide more code reuse than a traditional RTL design strategy
- have a synthesizable hardware implementation
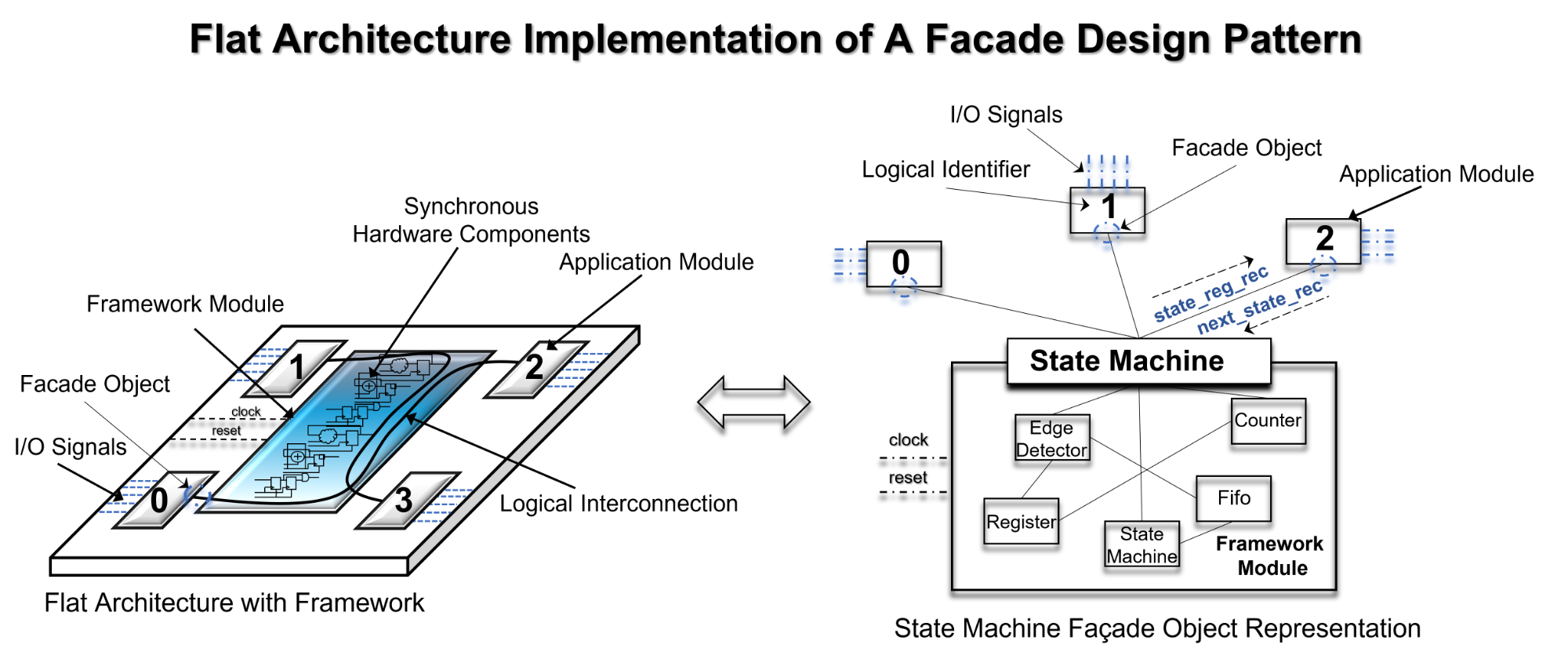
SpeakHDL uses a state machine as a façade object in order to provide the FPGA developer with a consistent interface to configure low level hardware components. Once a consistent interface is established, it is possible to configure synchronous hardware components with high level procedure calls. Every procedure call is parameterized with the
next state
and
state register
signals of a state machine. Increased HDL code reuse is achieved by creating an API library of reusable procedure calls in additional to traditional component reuse.
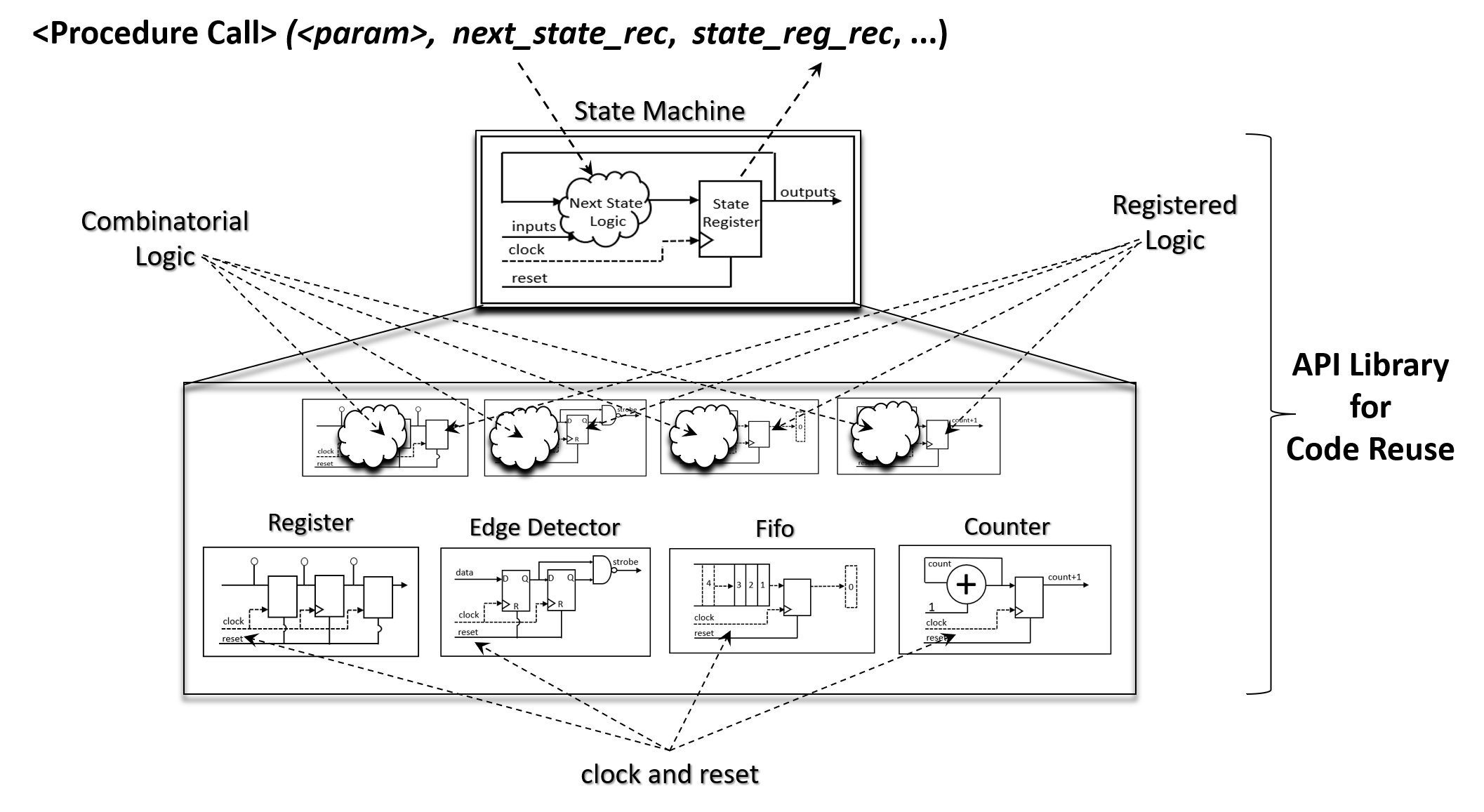
Graphically, it relatively straight forward to show that synchronous hardware components such as counter, fifos, registers, ect... are just specialized cases of a state machine where the combinatorial logic portion of the state machine differs. To utilize procedural procedural programming with a state machine as a fascade object, the caller simply passes input parameters to the procedure call which configure the state machine's combinatorial logic and read the registered logic as the output.
It can also be shown graphically that the
clock
and
reset
signals are common to all synchronous logic components allowing for a design simplification if the
clock
and
reset
are managed within the API library. In addition, separating the combinatorial logic from the registered logic suggests a consistent HDL code structure for the design pattern.
SpeakHDL is a Transparent Addition to Text Editors
SpeakHDL is a Transparent Addition to Text Editors:
From a users stand point, SpeakHDL is essentially just a background application running along side a text editor that enforces a specific VHDL coding structure. Consider the normal FPGA design flow, where a text editor is used to create some
.vhd
files which are subsequently used as input to a simulation and synthesis tool chain.
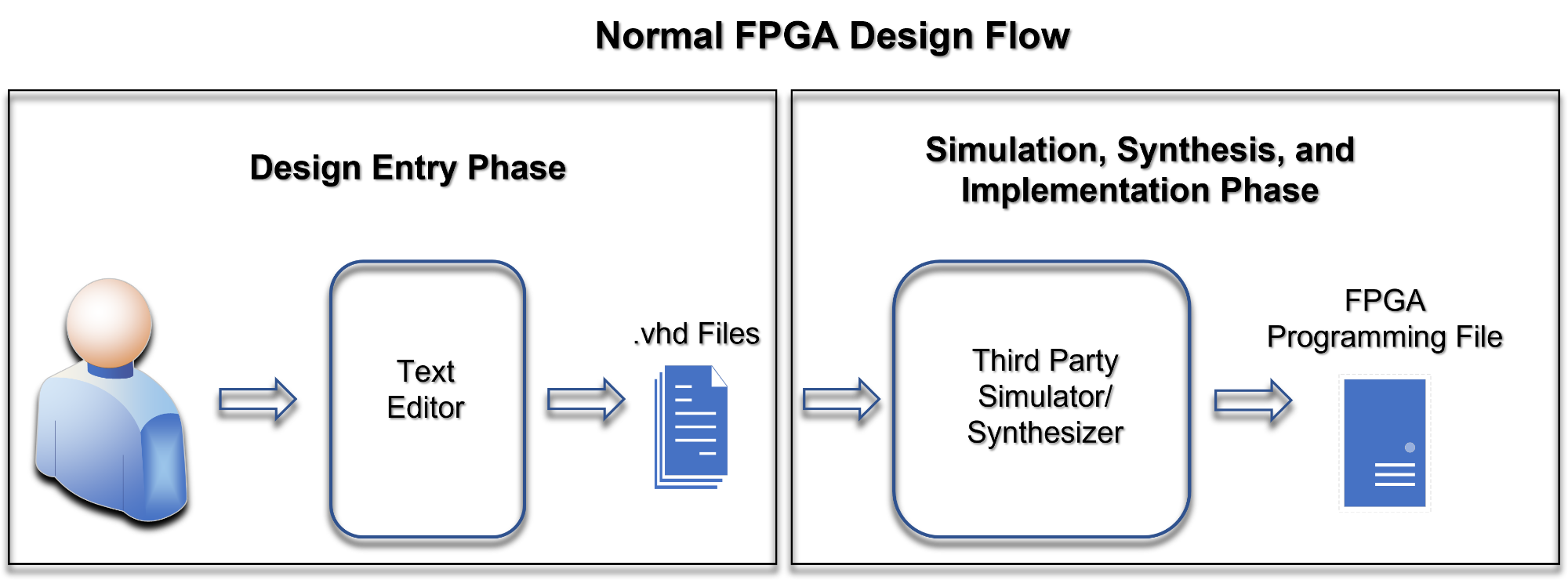
SpeakHDL does not change that flow. SpeakHDL serves an entry point for scripting which helps speed up development time. User commands can either be given by voice or by typing on the last line of the editor. When a command is recognized, SpeakHDL writes to one or more design files and updates the text editor with the new file structure.
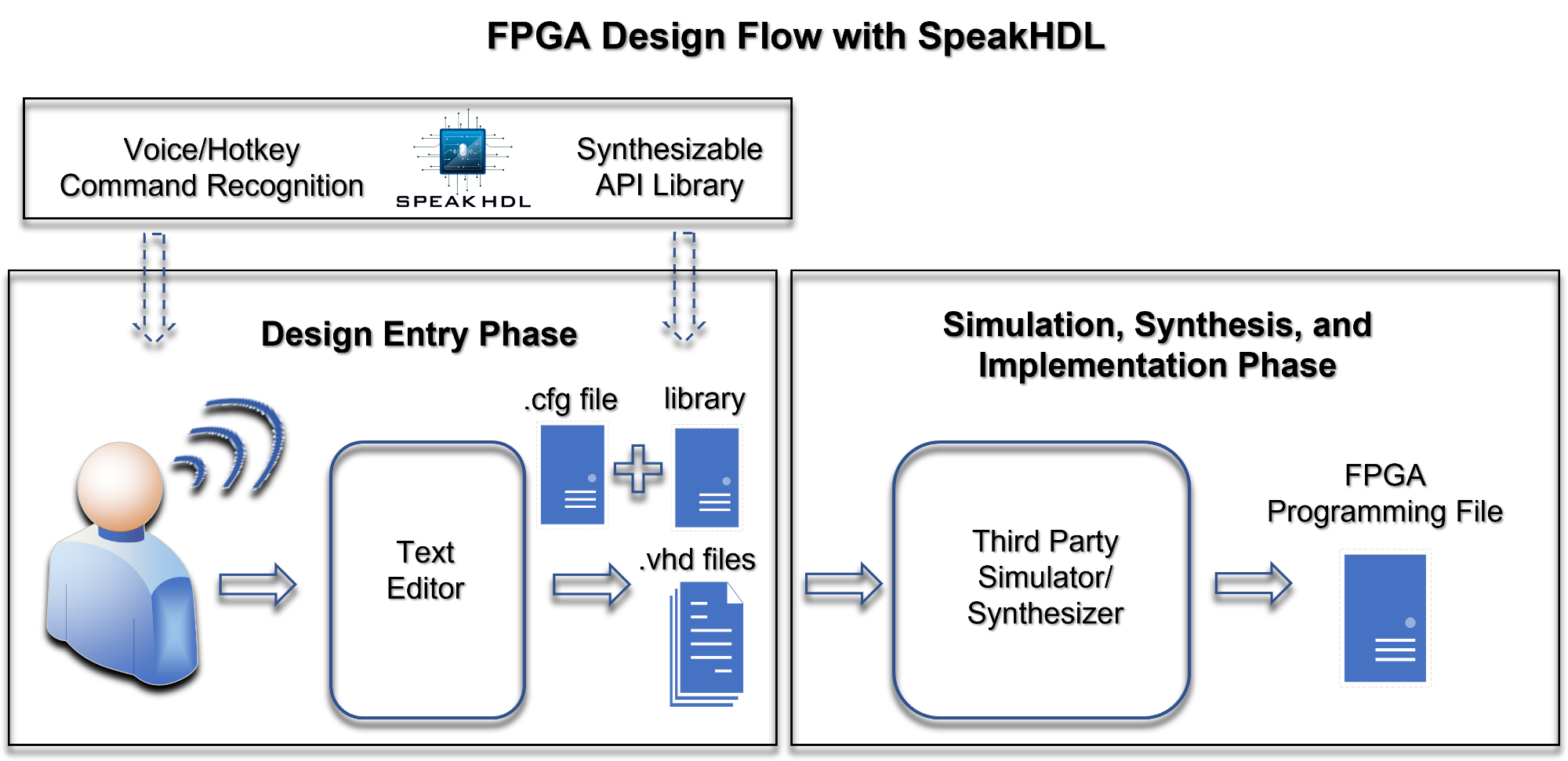
One of main advantages of using SpeakHDL over many GUI based FPGA design approaches is portability. All that is needed to run SpeakHDL is a text editor with a minimal set of features and an API library targeted for a vendor specific toolchain. Because the output of SpeakHDL are just text files containing native VHDL source code, it is possible to use SpeakHDL in a browser based text editor with no software installation or OS dependencies.
SpeakHDL Provides Meaningful Semantics
SpeakHDL Provides Meaningful Semantics
SpeakHDL's use of user commands and procedural programming is not only productive for FPGA design, but also provides more meaningful semantics than a traditional RTL coding style. Consider the SpeakHDL command sequence and the resultant VHDL code:
Voice Commands
- "restart from scratch"
- "configure state machine"
- "transition"
- "count thirty-three point two micro-seconds"
- "goto state one"
- "next state"
- "read fifo data"
- "count one twenty eight"
- "next state"
- "conditional transition"
- "goto state zero"
- "when shared register one equal to one"
- "ok"
Hotkey Commands
- restart
- sm
- tr
- count 33.2us
- goto 1
- n
- rf
- count 128
- n
- ct
- goto 0
- when shared_register(1) = 1
- ok
SpeakHDL Provides Meaningful Semantics
SpeakHDL Provides Meaningful Semantics
One could argue that any developer with a modest software background could figure out the intent of the VHDL code. The use of the
TRANSITION
procedure call handles state transitions which are only a function of time and the
CONDITIONAL_TRANSITION
procedure call replaces the need for an '
if-then-else
' statement when a state transition is dependent on a signal.
Command based programming provides a mechanism to easily
learn the API
without generating VHDL syntax errors. It eliminates the need to memorize the number, order, and data types of the parameters for each procedure call.
SpeakHDL Increases HDL Code Reuse
SpeakHDL Increases HDL Code Reuse:
Traditional HDL code reuse is obtained primarily through the use of
components. Component reuse is ideal for FPGA developers wishing to reuse local functionality. However, it is the integration and control of these components that often leads to an adhoc FPGA design with
tightly coupled
modules requiring a massive amount of signals declarations.
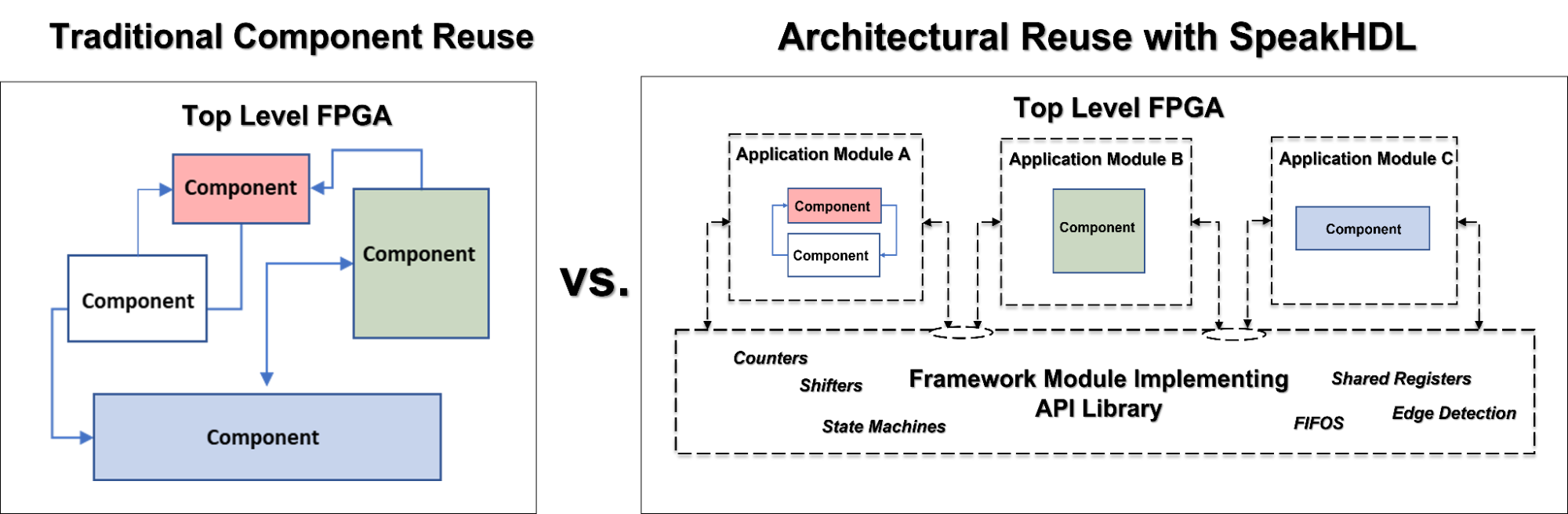
SpeakHDL adds to the traditional component reuse model by allowing for architectural reuse within an FPGA design. SpeakHDL provides a
reusable framework
that handles control and communication between
application modules
in a uniform way through the use of
overloaded procedure calls
. This improves VHDL code readability,
loosens the coupling
between application modules, and dramatically reduces the number of signals that need to be declared for interconnection purposes.
SpeakHDL Productivity Strategy
SpeakHDL Productivity Strategy
SpeakHDL's approach to FPGA design productivity is to provide the developer with an API and an
architectural framework
that can achieve more code reuse than traditional FPGA design strategies.
SpeakHDL makes use of proven software abstraction techniques to hide FPGA design complexity
by:
- Using a common port interface for all application modules that use the design pattern
- Utilizing a single VHDL process model
- Using procedural programming for high level data flow
- Abstracting the clock signal and reset signals into a larger data structure
- Forcing a separation between sequential logic and combinatorial logic
-
Using commands to avoid VHDL syntax errors invoke backend scripting
- Treating testbench development in the same manner as developing any other application module
SpeakHDL has Academic Value
SpeakHDL has Academic Value
It is generally accepted that that there are three modeling styles for HDL designs.
- Behavioral
- Structural
- Data Flow
Procedural programming using a facade design pattern would fall into the category of Data Flow Modeling. Data Flow Modeling provides a way to describe how data flows within a design and is independent of any HDL programming language and any particular programing constructs using to implement it. This should be contrasted with a Structural Modeling architecture where there are only component instantiations and signal assignments.
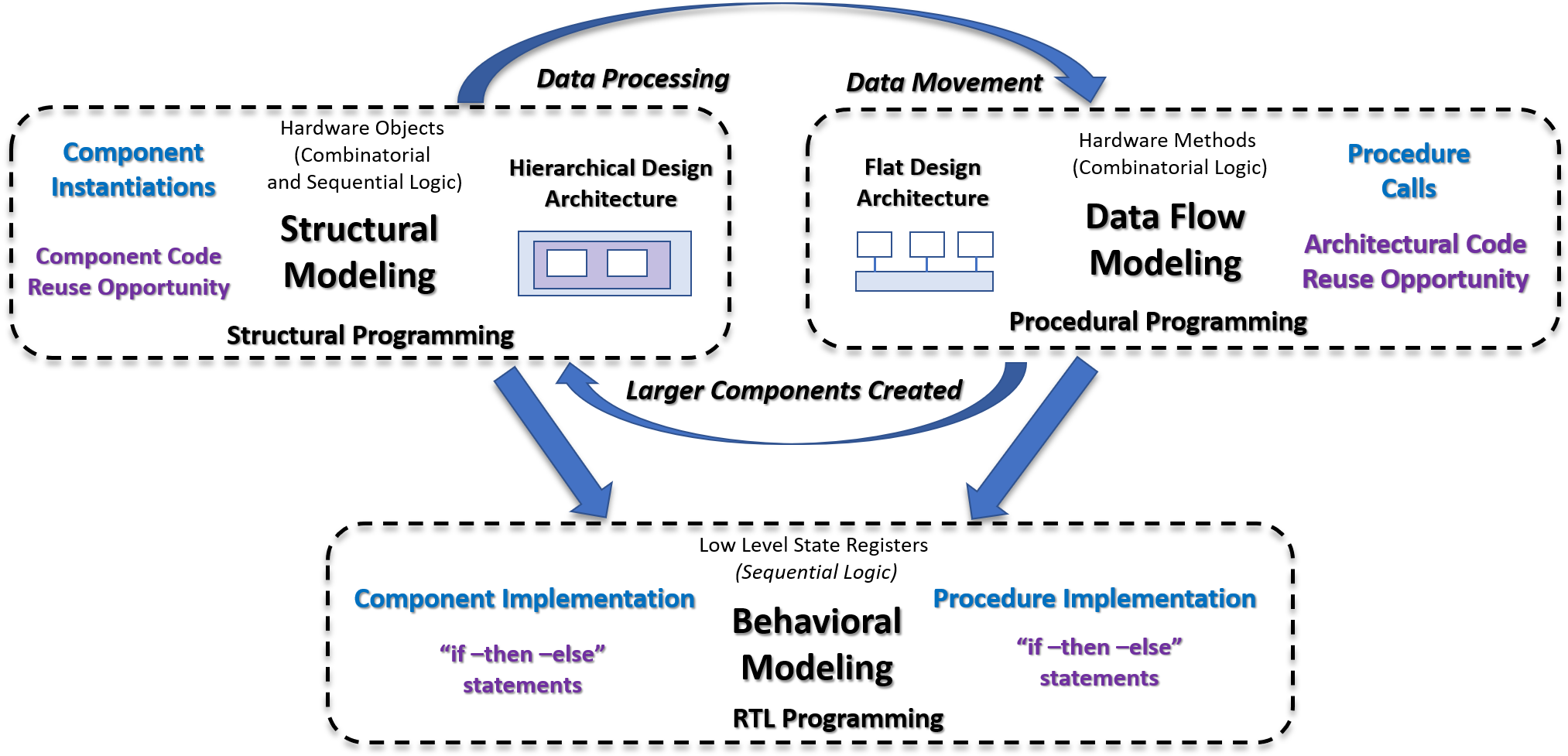
The SpeakHDL design pattern with a flat design architecture describes not only how data is moved throughout an FPGA design, but also how that data is controlled. This leads to an architectural code reuse opportunity whereas a traditional hierarchical design strategy leads to a only a component code reuse opportunity.
- See also
- Terminology and Definitions
